Case studies are one of the most effective ways to turn hesitant leads into customers. Some people even go as far as saying that a good case study is as effective as a personal recommendation.
Yet the problem is that because case studies are a chance for you to shout about your results, most companies end up producing the same sort of content. This is often along the lines of ‘‘Here’s How we Saved this Client a Million Dollars”.
The stats are one part of a case study that almost everyone gets. Most case studies struggle to get past the headline number. As a result, they miss out on the customer journey. In this guide, I’ll share with you how to write a long-form case study that tells a story and is relevant to potential clients. I’ll cover why you need to do this, and how, in the sections below.
What type of case studies you need
If you are running a company, you probably have a diverse client base. For example, the marketing agency that I consult for does content marketing and SEO consultancy work with a number of banks, Software as a Service companies, and enterprise level bricks and mortar companies. These clients operate in different verticals. While the overarching problem they face is often the same, their pain points are different.
The case studies you create for your business should reflect the range of clients you work with. To make them as relevant as possible they need to incorporate these different pain points within the copy. The closer you can align the case study with the problems a certain type of client is facing, the more impactful the case study will be.
Ultimately it is this relevancy that can be the difference between you winning a contract or losing it. For this reason, I strongly recommend creating a range of case studies that reflect the diversity of your clients.

You can see how Hubspot have taken this approach with the case studies they have on their site. The case studies cross eight different niches. The number of verticals reflects the diversity of their client base.
How to prepare your case study
Now, case studies obviously require a little bit of research on the client. The most powerful case studies mirror the customer journey of a client from consideration through to purchase. This means looking at the following:
- The problem they were facing when they contacted you
- What it was like to work together with you
- What was the impact of your work
Your aim is to get past the headline figures. For example, the end result of your work together might be a headline figure – $100,000 saved. But how that revenue is used, for example enabling a company to hire another employee, is a fact that could resonate with other potential clients. It is this combination of data and insights that provide a powerful case study.
The best way to get this information is a combination of surveys and interviews. A good survey will help you build a picture of the clients experience working together with you. The interview is where you ask pertinent questions that help fill in the finer details.
The kind of information you are looking to collect through your survey is a mixture of qualitative and quantitative data. Quantitative, which is all that numerical stuff. Things like money saved, money earned, or additional traffic brought to a website.
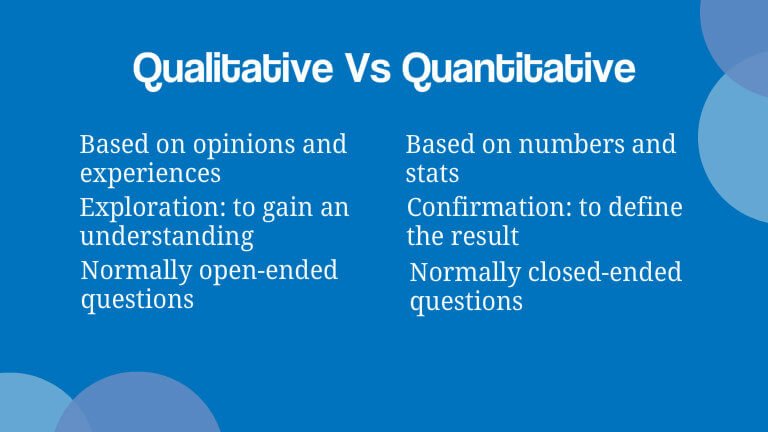
Qualitative data is wordier. This includes things like clients’ sentiments, personal experiences and lessons learned. To collect this information you need to ask the right questions.
You can loosely divide your survey questions into open or closed-ended. Closed-ended questions usually end up with ‘yes’ or ‘no’ answers. Asking someone to rate something on a scale of 1-5 is also a closed-ended question.
Open-ended questions are much more unpredictable. This looks like something along the lines of ‘How do you feel about …?’ The person on the other end could really come out with anything.
Ideally, you want less than 20 questions in your survey. They should be a mixture of open-ended questions and close-ended questions. The aim of these questions, as I mentioned previously, is to build the framework for your story. You want to collect the key facts and get insights you can use for the follow-up interview.
What questions to ask in your survey
When creating your survey questions you want to ask questions that follow the outline of the user journey. This essentially means covering those three points that I listed above and using a mixture of closed and open-ended questions.
The questions you pose in your survey should be specific. Break down big points into multiple questions. This is useful for customer satisfaction survey because each question provides insights into a different aspect of your business.
So, for example, you might break down the question, “why did you choose to work with our company?” to:
- What problem were you facing before you started working with us?
- What would have happened if you couldn’t solve the problem?
- What factor convinced you to choose our company over a competitor?
You can see how these three questions dig a little deeper. You could, of course, use the same approach with close-ended questions. Using this approach you can acquire information you can then use in the follow-up interview.
How to turn your case study into a story
It’s a generally agreed fact in copywriting circles that the amount of copy you need is proportional to the cost of the product or service you are selling. The more expensive the product or service the more you have to explain, show, educate and convince a prospect to make a purchase.
If you’re going to write a long piece of content you need to make it interesting. This is where storytelling comes into play.
Our lives are based on stories. We read stories in magazines, online, in the newspapers and watch made up stories on TV. Stories draw you in. Research by Jenifer Aaker, a professor of marketing at Stanford Business School, found that a story is significantly more memorable than facts alone.
Moreover, setting a case study within the framework of a story provides you with an opportunity to tap into emotional triggers. This is important given the fact that we make decisions based on both emotional and rational factors.
So you can think of it a bit like a glowing review from a customer, except you’re in control. That’s not to mention a whole range of extra benefits. Case studies are inherently good for natural keyword targeting. They’re also a great way to build client relationships.
Pulling it all together
Once you’ve got all of your data lined up, writing your case study is a breeze. Like all content, the first thing you need is a compelling headline. The example I gave at the start of this article were obviously jokes, but they’re also a pretty good indication of what you want to aim for.
The goal is to draw people in, so it’s good to try and squeeze in the kind of results they can expect from you. Even if it’s not a million dollars. Utilise the framework of a story to lead them towards your end goal. Finally, you hit them with a call to action.
You can see how I used this formula for a case study that I created to promote the software promos that my partner and I run.
- Start with a headline figure
- Place the case study within the context of a story
- Include insights from the person you worked with
- Provide proof in the form of screenshots
- Finish with a call to action
I link to this case study in the postscript of emails when I’m pitching my service. The majority of people I subsequently speak to read the piece. I know from discussing it with people I’ve worked with that the case study played an important role in their final decision.
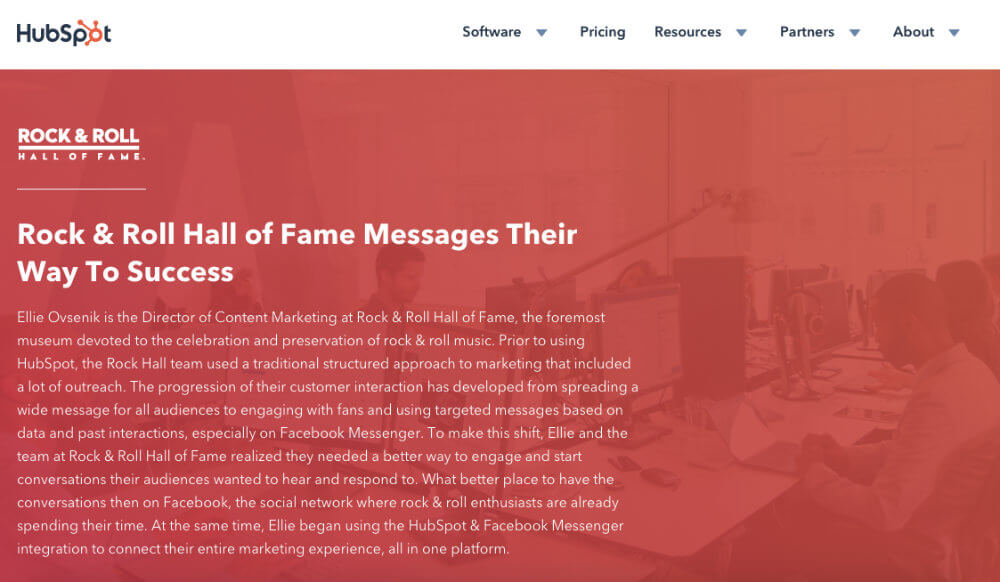
Hubspot utilizes a similar approach. Their case study for Rock & Roll Hall of Fame is a good example. They have an above the fold synopsis of the case study, followed by the headline figures and an extended piece of copy. It’s a nice format that satisfies the needs of scan readers and people who like to investigate before they make a decision.
Remember that design can play an important part in your case study. You want to highlight the key facts for people who are just going to scan read your content. You can do this with a well laid out case study. Below is an example of a custom page design that I created for a previous client that highlights all of the key facts above the fold.
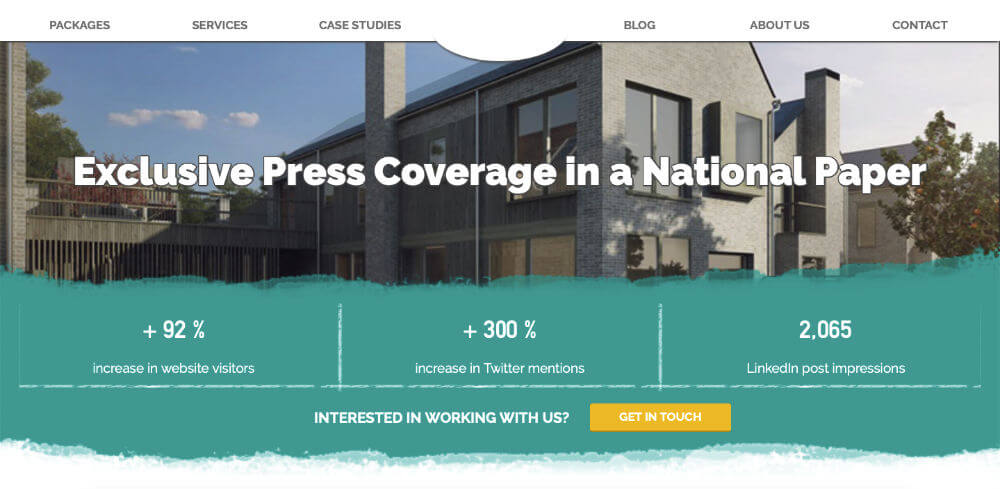
The core part of the case study is for people who want to have access to as much information as possible before they make a decision. Don’t be afraid to have 1,000 words or so of content. Just make sure that you apply copywriting principles, like using heading to break up the text, if you do so.
Wrapping up
We said earlier that surveys and case studies tie together nicely because one generates data and the other presents it. This a pretty straightforward relationship, but it seems like not everybody has gotten the memo.
I’m sure you’ve seen any number of boring case studies which say next to nothing. This happens when people know they’re supposed to write case studies, but they’re not really sure what to include. Or they might know what they want to say, but they don’t have any compelling quotes or statistics to back it up, so their case studies have very little real-world impact. This is why surveys and first-hand data is so crucial to creating a compelling case study.



